Vaccination Information Service

Whom do you trust, nature or man?
Do vaccines protect against diseases at all?
Bronwyn Hancock 25/1/99
Almost all of us have grown up knowing that our developed world suffers so much less from diseases than in the past, and we have happily accepted what we have been told, which is that the reason is vaccination. This is certainly what I assumed before I ever started looking at it.
In reality, however, it turns out that there is no scientific evidence that vaccines are at all effective, from a statistical OR immunological point of view. In fact unfortunately there is evidence that they are even counterproductive, in relation to the very diseases they are supposed to be protecting against. I will address these points of view in turn. Within each one I will address the evidence for their ineffectiveness first, then for their counterproductivity, under the following headings…
Statistical evidence indicating ineffectiveness
Statistical evidence indicating counterproductivity
Immunological evidence indicating ineffectiveness
Immunological evidence indicating counterproductivity
Appendix: Statistics.
Statistical evidence indicating ineffectiveness:
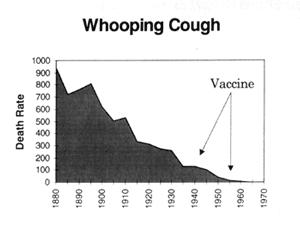
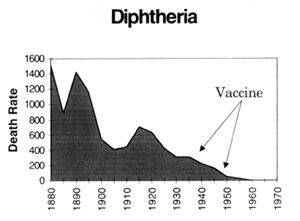
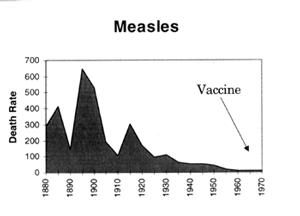
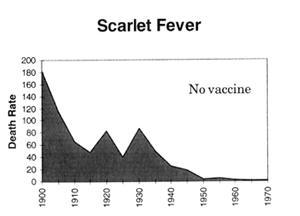
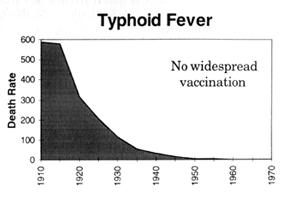
Looking at it from a statistical point of view, the statements we keep getting that cases/deaths declined since the introduction of vaccines are meaningless, because they were ALREADY declining, in fact they had already dropped by more than 90% this century by the time the vaccines were introduced.
This is clearly illustrated in the following graphs which are plotted using figures from the Commonwealth Year Book, the Australian Bureau of Statistics and the Commonwealth Department of Health and Human Resources. (Source - "Vaccination: A Parent's Dilemma" by Greg Beattie.) The arrows indicate where universal routine vaccination programs began. Death rates are per million:
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
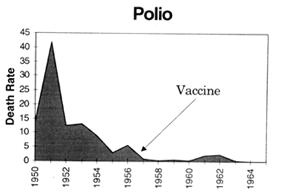 |
The only "evidence" that is ever provided to the public for their effectiveness (and even then not often!) is that SOME graphs will portray an actual acceleration in the decline in the number of REPORTED cases of a disease after the introduction of the vaccine (or an increase in reported cases after compliance falls). However there are many facts that all tend to undermine the significance of this "evidence". These include the following:
- There was no parallel effect on death rates, which are a more reliable measure than reported cases (which are subject to the skill and motivation of general practitioners),
-
The diagnostic guidelines given to doctors were supplemented with "No history of vaccination", when the vaccine was introduced. Even apart from that, doctors are taught that vaccines are effective so when they see an illness in a child who has been vaccinated, they conclude that it must be something else. A perfect example is Hib meningitis. When an Hib vaccinated child contracts meningitis, they are unlikely to test for the presence of Hib, so because several other types of bacteria can be present at the same time, it is not Hib but other bacteria that get the blame,
Other examples are whooping cough being called “croup” when it occurs in vaccinated children, and diphtheria being called such names as “epiglotitis”, or, as in this case, described in “Raising a Vaccine Free Child”, by Wendy Lydall (2005, pg 68),
‘Her aunt had nursed diphtheria cases in Britain in the 1950s, and she said that her niece had the typical symptoms of diphtheria. The girl was flown by helicopter to a bigger hospital in Auckland, where they took a swab from her throat and confirmed diphtheria. When they learned that the girl was fully immunised, one of the doctors said to the mother, "Then it can’t be diphtheria." They changed the diagnosis to bacterial tracheitis.’
-
Doctors, who base their diagnosis on symptoms, can be misled by the distortion of the symptoms due to damage of the immune system by vaccines, e.g. not getting a rash with measles. Consequently they are less likely to correctly identify the virus or bacteria that is present in such individuals,
-
It is well documented that doctors, who are not legally obliged to report any cases at all, under-report cases in vaccinated c/f unvaccinated individuals (Pediatrics 1998;102:909-912). One study showed underreporting by GPs could be as much as 24,000 times. (Br J Clin Pharm 1997 Feb;43(2):177-81). They are also far more strongly encouraged to report cases after falling vaccination compliance, the reason given being the so-called fear of the authorities that there will be a bigger epidemic than usual (see Am J Epidemiology 1984 – article by Gordon Stewart). Of course, statistically speaking, this is a self-fulfilling prophecy.
-
In outbreaks of diseases, figures often indicate that the percentage of cases vaccinated are as high, sometimes even higher than the uptake levels in the community, e.g. 87% of cases of whooping cough in South Australia from 1990 to 1996 were fully vaccinated (which was far higher than the vaccination coverage rate in the community, including only 61% in 0-6 year olds), in U.S. outbreaks 98%, up to even 100% (Illinois 1984, Corpus Christie 1985 – measles) of cases have been fully vaccinated (Bull WHO 1993). In fact Sweden stopped whooping cough vaccination in the 1970s after observing the percentage of cases vaccinated (84%) was the same as the vaccination compliance in the community. (See Appendix for more figures),
-
Sometimes the vaccination programs are implemented/stopped at peak/trough times of the natural 3-4 year disease cycles (possibly deliberately on some occasions), with the inevitable wane/wax phase of the cycle being falsely attributed to vaccination/lack of vaccination, and
-
These disease cycles, caused by the number of susceptibles gradually increasing over time, and decreasing again when outbreaks occur, have not increased in length with the use of vaccines.
If you get into studying individual articles in medical journals, many of course claim effectiveness, but there are various unscientific methods researchers use to draw such a conclusion, other than those already covered above, such as
1) using toxic injections as "placebos" for their control groups. In many cases we can put the unscientific methods down to incompetence, but we really HAVE to wonder why they would deliberately give harmful substances to control groups,
2) looking back in the past at incidences
of a disease in the vaccinated vs unvaccinated ignoring the fact that those not vaccinated
would usually have not been vaccinated for a reason, e.g.
(a)already being immune-suppressed (quite possibly by another type or dose of vaccine!),
or
(b)low socio-economic status – these people are more susceptible due to poor
nutrition, etc.
3) having misleadingly
strict definitions of "vaccinated" cases, e.g. only where
i) the parents of the children REMEMBER vaccinating AND have their records (MJA 1995), or
ii) the person is old enough to have had all the vaccines (i.e. is not a young baby), or
iii) the person has been vaccinated within a given period prior to contracting the disease, or
iv) the person has been vaccinated right on time.
4) When vaccinated seropositive children don’t contract the disease in an outbreak, this is assumed to be because of being seropositive from the vaccine. Data on the children’s history of natural infection, which DOES normally bring immunity (this is common knowledge!), is not even collected.
We are STILL, after many decades, waiting for a randomised, double-blind placebo-controlled trial establishing the value of vaccines, but the pharmaceutical industry, the main provider of research funds (in fact it has now more blatantly taken over the research), will not do it, and amazingly justifies this by saying that to do it they would have to deny the vaccine to the control group, which is supposedly unfair to those people! Thus we are given a circular argument.
Statistical evidence indicating counterproductivity:
Further, there is statistical evidence that they are actually counterproductive:
1) Outbreaks often occur soon after the vaccination programs (e.g. Corpus Christi, 1985 where, by the way, ALL those who contracted measles were vaccinated, the unvaccinated 1% did not!).
2) Whooping cough in the U.S. has been rising for the first time ever in recorded history since 1978 (or just after that to be precise), and consistently ever since. The 1996 level was the highest since 1967 (CDC MMWR Oct 31 ‘97). So what happened in1978? This was the year that the U.S. mandated w.c. vaccination for school entry. So much for the so-called "herd immunity" idea. In fact researchers worked out from hospital admissions that by 1985-1988 the rate had ALREADY reached what were in fact pre-vaccine levels (JAMA 1992), and the sustained increase has continued since, so, with a mandatory 5-dose course of DPT vaccination, the whooping cough rate now is FAR higher than before the vaccine was even introduced.
3) The dramatic fall in whooping cough vaccination compliance in the UK in the 1970s - after the revelation to the public that it causes encephalitis (brain damage) - was followed by a record long inter-epidemic period, and low death and complication rates in the epidemic that followed (Am J Epidemiology, 1984). (The high number of recorded cases, which goes against this trend, is explained in the previous section – point 4.). Similarly in Japan, DPT vaccination for under 2 year olds stopped due to the observed link to cot death, the incidence rate only climbed in parallel with the gradual climb in uptake rate as more and more toddlers reached 2 years of age (Pediatrics 1988 Suppl.).
4) I am told (but I haven’t been able/got around to confirm(ing) yet) that measles in Europe, having virtually died out, actually rose again when they started the measles vaccination programs
5) The age
distribution for the childhood diseases (i.e. whooping cough, measles, mumps, rubella and
chickenpox) has altered in highly vaccinated countries such that the highest incidence is
no longer at the desirable age of childhood, but in the more vulnerable infanthood. The
reasons for this appear, on the basis of the published medical literature, to be:
(a) the vaccines given to the infants increase the susceptibility to the diseases, and
(b) the vaccines that the mother had herself as a baby weaken the transplacentally
transmitted immunity that she is supposed to pass onto her infant to provide temporary
protection (this undesirable consequence of vaccination is well documented in the medical
literature.).
Adolescents are also increasingly contracting these childhood diseases, due most likely to
(a) the harm done to the immune system such that
the old "rule" that you only contract each of these illnesses once and, having
fully recovered, then have full immunity, does not apply now as much as it should, and did
in the past, and
(b) the likelihood (Dr Viera Scheibner’s well considered opinion based on her study
of almost 100000 pages of research on vaccinations) that the immune system development can
be retarded by the vaccines, so that by that late age it’s still only up to childhood
stage.
6) Due to the damage to the immune system, ONLY the vaccinated are contracting the atypical forms of the diseases, which are more serious than the typical forms, e.g. the rash in atypical measles moves in the wrong direction, heading straight for the vital organs instead of away from them, resulting in those serious cases of pneumonia, meningitis, etc, we keep getting told about. Ironically and misleadingly the establishment uses these serious cases to frighten parents into vaccinating! The derailing effect on the immune system is further evidenced by many published findings such as "The rate of complications among those who were immunised was greater than among those who were not and was significant" (Bull WHO 69(2): 1991 p213).
7) Some illnesses that we vaccinate against are themselves provoked by vaccines, and were not a problem until mass vaccination with other vaccines in the first place, since the organism involved is normally quite innocuous. Examples of this are Hib and poliomyelitis. (There is a reason why they call polio a 20th century illness!) With each of these, of course, they stopped diagnosing the illness as such once the vaccine was introduced. (For a wealth of references see chapters on these diseases in "Vaccination – A Medical Assault on the Immune System" by Viera Scheibner PhD)
8) When the immune system is functioning properly, immunity develops once a disease has been contracted. However, it has been found that vaccine recipients are not only still as susceptible to contracting the illness, but that they can contract it more than once. Dr Archie Kalokerinos reports that in the massive smallpox outbreak that occurred in the Philippines in the first decade of the 1900s (after a mass vaccination program!), it was documented that the ONLY people who contracted smallpox TWICE were the vaccinated.
Immunological evidence indicating ineffectiveness:
Looking at it from an immunological point of view, the only "evidence" that is ever provided for their so-called effectiveness is that the vaccination succeeds in stimulating the immune system to produce antibodies. In fact the degree of success in doing this is the way that the effectiveness is often measured. However a false assumption is being made that the IgG antibodies produced will bring immunity.
In reality the immune system is far more complex than this. It has actually been established that there are very many processes that the body needs to go through in order to develop immunity. One example, which is probably the best of these understood (immunologically speaking), is that, at the minimum, the activation of the secretory antibody IgA needs to occur, which has an important role in the whole process. This, and many other processes that occur in the outer levels of defence, are BYPASSED by injections.
Dr Peter Baratosy has drawn a good analogy, which is that vaccination is a bit like trying to get a car to move just by pressing on the accelerator without putting it in gear. It makes lots of noise but does not move a single inch.
*Recently (as of 16/7/2004), a woman with a PhD in immunology confessed that she was not in favour of vaccination. When asked why, she said "Well, looking at serum through the microscope I could see that the antibodies went right past the vaccine-injected antigens as if they weren't even there." (When she was then asked, "Would you be willing to put that in writing?" she replied, "No, I would lose my job.")
So, as Dr Archie Kalokerinos says, you can have tons of antibodies and still get the disease, even die from the disease. Dr Archie Kalokerinos also goes further to say that you can actually have NO antibodies and yet still not contract the disease when exposed. In fact most of the time that we are exposed to a foreign invader, it does not even reach anywhere near the deep level to which we are injecting it with vaccines – we deal with it easily in the outer levels and might even develop immunity just from that.
The polio vaccine is not an injection, but you still cannot artificially induce immunity whenever you want to, as the process depends on various dynamics which depend on the state of the body. Indeed many people actually contract polio from the vaccine, which also by the way contains a more virulent form than the normally harmless wild form, and the dose is not even small. Further, there are still very importantly all the toxic, sensitising substances being swallowed with it. Of course we will not suffer with polio anyway if we do not damage our immune system by interfering with it via other vaccines, tonsillectomies, antibiotics, etc, etc. Records indicate polio was not a problem in the past before all this interference started a century ago with the smallpox vaccine. The first recorded outbreak of paralytic polio was not until 1887, even though the polio virus itself has been around (as far as can be determined) for as long as man has. It is referred to as a 20th century disease.
Immunological evidence indicating counterproductivity:
Further, there is immunological evidence that vaccines are actually counterproductive. This evidence is the fact that they have a very well documented effect of sensitisation. Interestingly, immunologists themselves are said to feel uncomfortable about the fact that vaccine injections can only stimulate a significant IgG antibody response if they include toxic sensitising substances, referred to as "adjuvants", in the concoction ("Dirty Secrets", New Scientist, Nov 1996).
Sensitisation is really the OPPOSITE of immunisation. Immunisation is PROphylaxis, which means prevention. Sensitisation is another word for ANAphylaxis (to various degrees) which indicates susceptibility is in fact increased, and due to the derailment of the immune system it "panics" when we encounter harmless things (hence allergies, asthma, etc). This is a stress response that does not result in any positive resolution, because the immune system is confused and handicapped.
Similarly, vaccination leads to the development of autoimmune diseases because of this confusion, as a defect appears to occur in the immune system’s ability to tell the "good guys" from the "bad guys", so that the person’s own cells are attacked.
For more on the immunological fallacy of the vaccination theory, read "Vaccination: It's your informed choice" by Dr Peter Baratosy.
Apart from statistics and immunology, we
could also look at it from other points of view such as:
the fact that the vaccination idea falsely
assumes that germs are the cause of disease, instead of infiltrating the system and
flourishing as a result of it, so it misses the mark. Worse, vaccination is
counterproductive because it introduces toxic substances, which DO cause disease
(For more on the falsity of the germ theory, read
"Vaccination - The Hidden Facts")
Mother Nature’s rule that whenever we
do anything unnatural it will only harm us to some extent, not help us, as it will not fit
in with the design of the body, which is much more finely tuned than is appreciated by
most.
Rather than specific research findings in
themselves, one would describe these two statements as very credible theories which
provide a broad explanation for the many detailed specific statistical and immunological
observations that have been made and documented in medical research.
Appendix: Statistics.
Here are the known vaccination rates (according to questionnaires returned by parents) amongst the cases of measles and whooping cough in recent years in the states in Australia which have collected the data (Note that the measles figures apply only to those old enough to have been vaccinated - the first measles vaccine is not given until 12-15 months of age.) :
| Infection | State | Period | % cases fully vaccinated |
| Whooping Cough | S.A | 1990 - 1996 | 87% |
| " | Vic | 1995 | 76% |
| Measles | S.A | 1993 - 1996 | 50% |
| " | Vic | 1995 | 79% |
| " | Vic | 1996 | 74% |
| " | W.A | 1996 | 67% |
| " | Western Sydney outbreak | 1993 | 78% (MJA 1995) |
These rates, which are similar to, in fact some higher than, the rates of coverage recorded in the states as a whole, have been obtained from the various states’ health departments. Most are in Greg Beattie’s book "Vaccination - A Parent’s Dilemma". The book also has many other figures from other countries, which, not surprisingly, show a similar trend.

